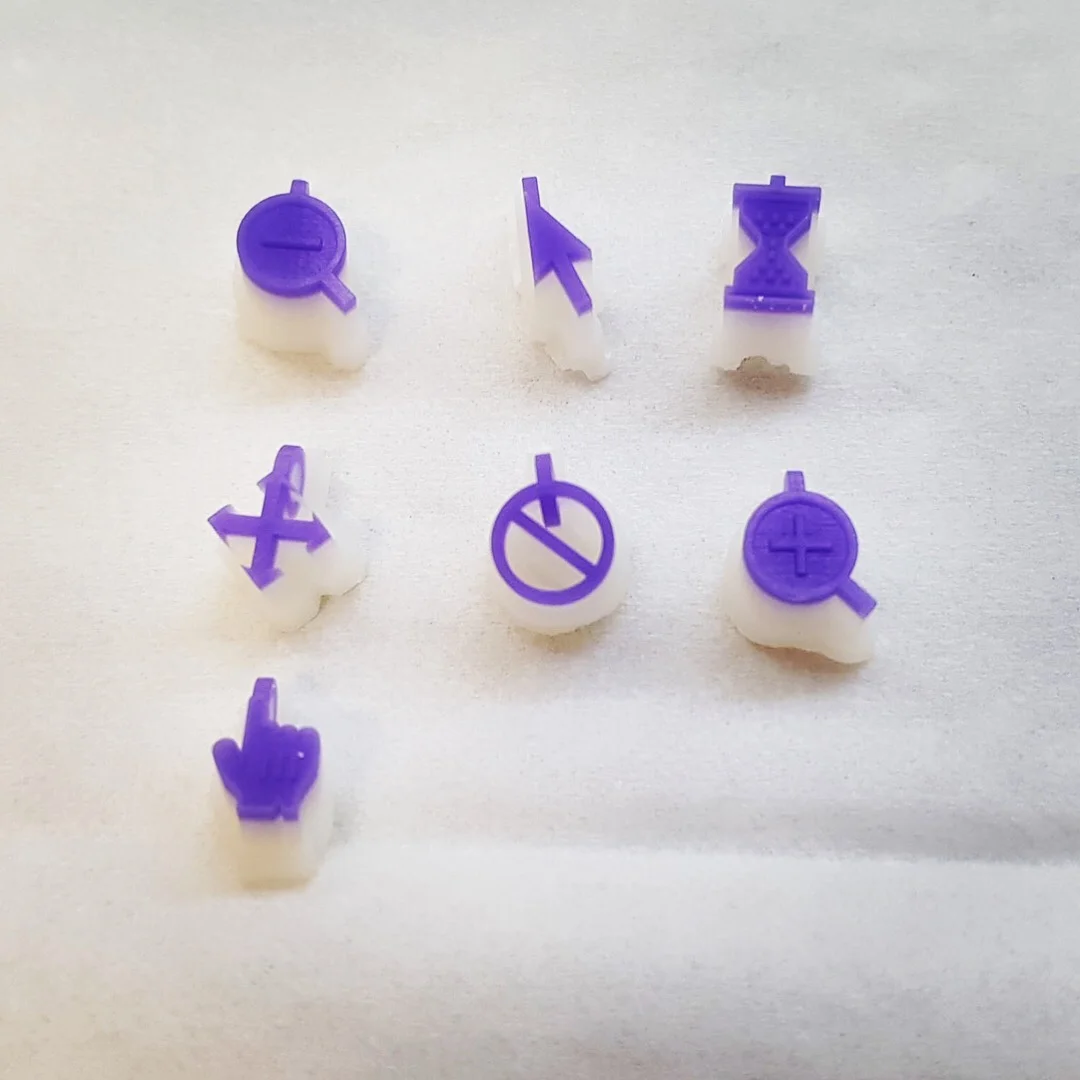
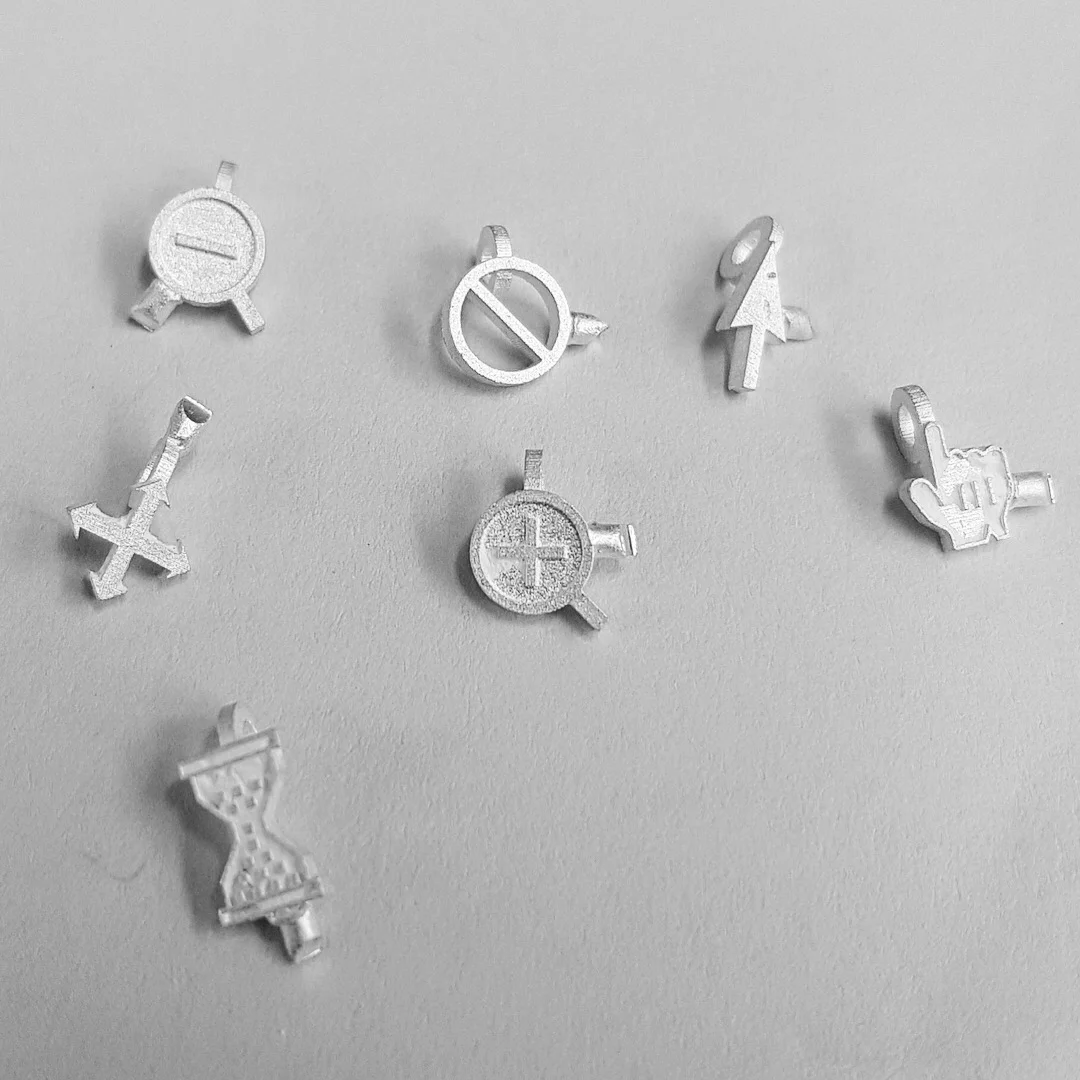
We’re exploring the capabilities of the latest 3D printing methods and printers.
What exactly is 3D printing? We’re so glad you asked...
What is it?
3D printing is the action or process of making a physical object from a three-dimensional digital model, typically by laying down many thin layers of a material in succession. It’s also called “Additive Manufacturing” - because you are adding material to manufacture a shape vs taking material away.
How does it work?
There are several types of printers and materials you can print.
Some printers extrude layers; like squeezing a tube of toothpaste, and others fuse liquids or powders together in layers with lazers, lights or even electrons.
Who uses 3D printing?
Product designers for creating quick prototypes of their products
Surgeons for medical implants and prosthetics
Dentists for dental implants
Spaceships and Automotive
Architects - concrete and specific designs for buildings.
Scientists - biology, nano things and new materials
Fashion designers - Clothing
Chefs - Food
Why is it awesome?
How 3D printing has been used to date
3D printing has sped up prototyping for products. Designers can 3D model a shape, print it in minutes then test it out and iterate.
What’s the latest 3D printing inventions, discovering and benefits?
Metal 3D printing is starting to create efficiencies for multiple industries. For example, car/spaceship/airplane parts used to have to be made out of several parts - but now you can 3D print all in one - speeding up manufacturing processes by reducing assembly time. 3D printed parts are stronger because they have less joins (therefore less weak points).
Mixed materials and colours - some printers enable multiple materials and colours to be printed at the same time - think knitting with three colours - adding the colours in when the pattern requires it.
What is the future of 3D printing?
Companies could sell you a ‘file’ that you get printed at your local printer. Less shipping, transportation, fuel consumption and less waste.
3D printed body parts
Bigger things! More houses and cars and big stuff!
Types of 3D printing
* = what HIJ is currently using
Stereolithography(SLA)
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Fused deposition modeling (FDM)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)*
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Electronic Beam Melting (EBM)
Laminated object manufacturing (LOM)
Binder Jetting (BJ) Technology
Material Jetting (MJ) Polyjet and Wax Casting Technology*
Textures
Titanium is 3D printed via powder bed fusion - direct metal laser sintering (DMLS or SLS) giving a textured finish
Silver is cast from 3D printed wax - via material jetting giving a smooth finish